How to Improve My Citation?
How to Increase Citations: 20 Proven Strategies for Researchers (2026 Update)
In the competitive landscape of modern academia, your research's impact is often measured by a single, powerful metric: your citation count. Whether you are a PhD student looking for a post-doc position, a researcher aiming for a professorship, or an applicant for an EB-1 visa, increasing your citations is essential for demonstrating national or international acclaim. Read more here on why your total citation is important.
However, high-quality research doesn’t always guarantee high citation numbers. You need a proactive strategy to ensure your work is seen, read, and cited by your peers. How to improve my citation? below you will read 19 effective strategies to increase your citation count on Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science.
Table of Contents:
a) Prioritize High-Impact and Timely Research 🥇
b) Optimize Your Publishing Strategy 👨💻
c) Enhance Your Digital Presence and Networking 👨🏫
d) Optimize for Search Engines (Academic SEO) 🔍
e) Use Specialized Visibility Services for Citations ✍️
Frequently Asked Questions about How to Improve My Citations ❓
a) Prioritize High-Impact and Timely Research
The foundation of a high citation count is the relevance of your work. Research that addresses "hot topics" or solves long-standing problems in your field naturally attracts more attention.
1- Novelty Matters: Pioneer research in emerging fields—such as AI ethics, sustainable energy, or novel biotechnologies—tends to receive a surge of citations.
2- Quality Over Quantity: It is better to publish one high-quality, comprehensive study than several low-impact papers. Focus on work that provides a definitive answer or a significant new methodology that others will need to reference.
b) Optimize Your Publishing Strategy
Where and how you publish can significantly influence your visibility.
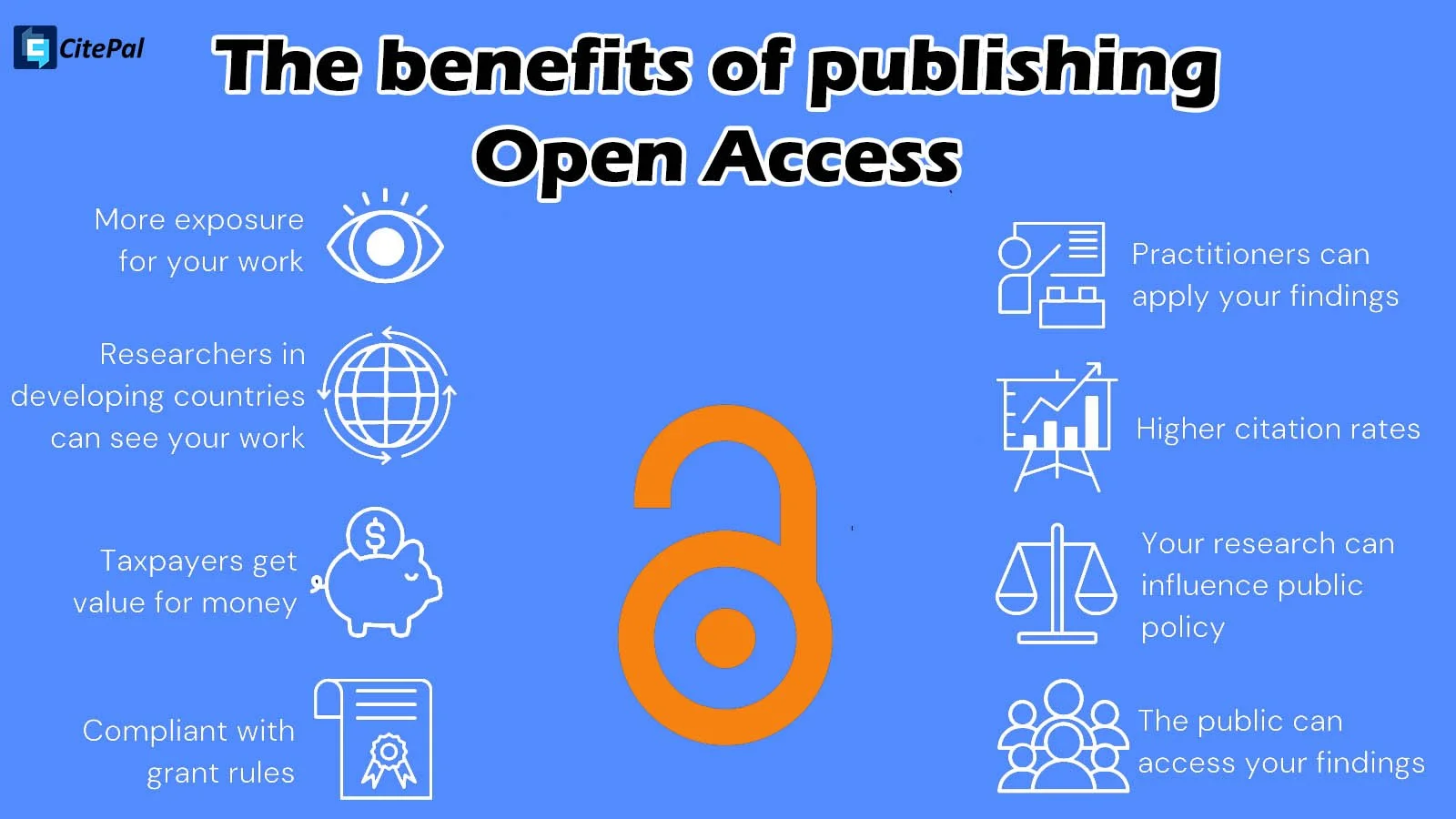
3- Leverage Open Access (OA): Studies consistently show (check this published in Science) that open-access articles are cited more frequently because they are accessible to everyone, regardless of institutional subscriptions.
4- Utilize Preprints: Don’t wait for the months-long peer-review process to end. Sharing your work on preprint servers like arXiv, bioRxiv, or SSRN allows other researchers to find and cite your work much earlier.
5- The Power of Review Papers: Review articles often garner more citations than original research because they serve as a foundational "one-stop shop" for other researchers entering the topic.
6- Write Methodological Papers: If you develop a new technique or software, a paper focusing specifically on the method often gets cited more than the individual results it produces.
7- Target Special Issues: Submitting to a "Special Issue" of a journal often yields higher visibility than a standard issue because the journal promotes the collection as a focused "hot topic."
8- Optimize for AI Discovery Tools: Modern tools like Elicit and Consensus look for clear "claims." Ensure your abstract has a direct "We find that..." sentence to help AI tools surface your work to researchers.
c) Enhance Your Digital Presence and Networking
If your work isn't visible, it won't be cited. Engaging with the scientific community is no longer optional; it is a necessity.
9- Academic Social Media: Use platforms like LinkedIn, X (formerly Twitter), and ResearchGate to share your latest publications. A well-placed post about your findings can lead to hundreds of new readers.
10- Conference Participation: Presenting your work at international conferences allows you to build a network of colleagues who are more likely to remember and cite your work when they write their own papers.
11- International Collaboration: Papers co-authored with international teams consistently show higher citation counts due to the wider reach across multiple geographic networks. When presenting, include a QR code on your final slide that links directly to the full-text paper or your ResearchGate profile.
12- Strategic Self-Citation: Ethically cite your previous relevant work. This builds a "research thread" that helps readers follow your trajectory and find your older, foundational papers.
13- The "Reciprocal Citation" Effect: Cite the leaders in your field and those whose work you are building upon. Often, these researchers set up "citation alerts" and will be the first to read (and potentially cite) your new work.
14- Code & Protocol Sharing: For technical fields, sharing your code on GitHub or OSF makes your research "reusable," leading to citations from researchers who build upon your tools.
15- Data Sharing (with DOIs): Linking your raw datasets in repositories like Zenodo or Figshare can increase citations by up to 25%. Researchers often cite the paper to use the data.
d) Academic SEO: Optimizing for Google Scholar & Scopus
Just like a website, your paper needs to be discoverable via search engines.
16- Keyword Repetition in Metadata: Don't just pick keywords; use your primary 3–5 keywords 3–6 times throughout your abstract. This helps search algorithms (like Google Scholar’s) rank you for those specific terms.
17- Consistent Author Identity: Ensure your name is formatted the same way across all publications and platforms. Using an ORCID ID is the best way to prevent your citations from being split across different profile variations.
18- Declarative Titles with Colons: Research indicates that papers with a colon in the title (e.g., "Keyword: A Study of...") get cited more than those with question marks or hyphens, which can sometimes break indexing.
19- Metadata Hygiene Audit: Periodically check Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar to ensure your papers aren't "orphaned" or split due to typos in the journal's indexing or your affiliation.
| Strategy | Actionable Steps | Impact on Citations |
|---|---|---|
| 1- Declarative Titles | Use colons and strong results-oriented phrasing (e.g., "Keyword: The Effect of..."). | Improved indexing and higher click-through rates in database searches. |
| 2- Keyword Density | Repeat primary keywords 3–6 times in the abstract and metadata. | Higher rankings in Google Scholar and Scopus keyword searches. |
| 3- ORCID Consistency | Maintain a persistent ORCID profile and use a single name variation. | Prevents "orphaned" citations and ensures all credit aggregates to one profile. |
| 4- Metadata Audit | Check Scopus/Web of Science for split profiles or indexing typos. | Ensures the h-index is calculated accurately across all platforms. |
| 5- Preprint Utilization | Upload early drafts to arXiv, bioRxiv, or SSRN. | Builds early momentum and allows citations to start before formal publishing. |
| 6- Green Open Access | Self-archive accepted manuscripts in institutional repositories. | Removes paywalls, making research available to the global scientific community. |
| 7- Data Sharing | Upload raw datasets to Zenodo or Figshare with a dedicated DOI. | Research with shared data receives up to a 25% increase in citations. |
| 8- Code & Protocol Sharing | Share software, scripts, or lab protocols via GitHub or OSF. | Increases "reusability," prompting citations from researchers using your tools. |
| 9- Review Articles | Synthesize existing literature into comprehensive review papers. | Review papers are "citation magnets" and serve as foundational references. |
| 10- Methodological Papers | Publish papers specifically describing a new technique or software. | Other researchers cite the method every time they use it for their studies. |
| 11- AI Tool Optimization | Use clear "We find that..." claims to help AI discovery tools like Elicit. | Ensures your work is surfaced by modern AI-driven research assistants. |
| 12- Special Issues | Contribute to journal special issues on "hot topics." | Higher visibility due to targeted promotion by the journal publisher. |
| 13- International Collaboration | Co-author research with international teams across different institutions. | Expanded geographic reach leads to higher global citation counts. |
| 14- Ethical Self-Citation | Strategically cite your own relevant prior work to build a narrative. | Helps readers discover your foundational research and track your progress. |
| 15- Reciprocal Engagement | Cite the leaders and active researchers in your specific niche. | Triggers citation alerts for those authors, increasing their awareness of your work. |
| 16- Social Media Promotion | Create LinkedIn carousels or X (Twitter) threads summarizing key findings. | Drives non-academic traffic and increases visibility among peers. |
| 17- Conference QR Codes | Add QR codes to posters/slides linking directly to your full-text PDF. | Immediate conversion of conference interest into paper reads and saves. |
| 18- Wikipedia Presence | Reference your findings in relevant Wikipedia articles where appropriate. | Generates high-volume secondary traffic and broadens public impact. |
| 19- Academic Profiles | Keep ResearchGate and Academia.edu profiles updated with direct DOI links. | Ensures your work is easy to find for researchers outside your institution. |
| 20- Visibility Services | Leverage professional organic boosting services like CitePal. | Guarantees visibility to reach citation thresholds for EB-1 visas and tenure. |
e) Use Specialized Visibility Services for Citations
Sometimes, even the best research needs a push to reach the right audience. Services like CitePal specialize in enhancing the visibility of your work. By ensuring your research is seen by the right academic circles, you can organically grow your h-index and total citation count, providing the "sustained acclaim" required for high-stakes applications like the EB-1 green card. Our end-to-end solutions for increasing the citation of your published articles can be found here.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions about How to Improve My Citations?
Why is citation count considered a critical metric for researchers?
Citation counts serve as a primary indicator of a researcher's academic impact and the relevance of their work within a specific field. Beyond personal prestige, a high citation count is often a prerequisite for securing research grants, obtaining tenure, and demonstrating "extraordinary ability" for high-stakes immigration paths such as the EB-1 or NIW visa categories.
How does publishing in Open Access (OA) journals impact my citation rate?
Studies consistently show that Open Access articles receive significantly more citations than those behind paywalls. By removing financial barriers, OA allows researchers from institutions with limited subscriptions, as well as the general public and policymakers, to read and reference your work immediately, leading to a broader and faster citation trajectory.
What is "Academic SEO," and why is it necessary?
Academic Search Engine Optimization (SEO) involves optimizing your paper’s title, abstract, and keywords to ensure it appears at the top of results in databases like Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science. Without strategic keywords and a clear, descriptive title, even high-quality research may remain "hidden" from researchers searching for that specific topic.
Can writing review papers significantly boost my h-index?
Yes. Review articles typically garner more citations than original research because they provide a comprehensive overview and serve as a "one-stop shop" for other researchers. By synthesizing existing literature, review papers often become the standard reference for anyone entering or working in that field, leading to a steady accumulation of citations over time.
How do citation visibility services like CitePal assist with EB-1 visa requirements?
For EB-1 visa applicants, demonstrating "sustained national or international acclaim" is vital. Specialized visibility services help by ensuring your work reaches the right academic circles through organic promotion and networking strategies. This professional boost helps researchers meet specific citation thresholds and h-index requirements that evidence the global impact of their work to immigration authorities.
Written by the CitePal Editorial Team, specializing in academic metrics and USCIS citation standards for EB-1A, EB-1B, NIW petitions, and citation boosting services. Our data is derived from 500+ successful applicant profiles.